PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
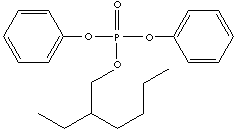
Diphenyloctylphosphate;
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Clear to yellow liquid
1.087 - 1.093
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
1.508 - 1.511
224 C
APPLICATIONS
Phosphate esters derived from Diphenly Phosphate are used as component of hydraulic fluids and lubricant oils. Tehy are mainly is used as flame retardants in many plastics and reins for the application of manufacturing electrical and automobile parts. They are used as flame retarding plasticizers or additives in cellulose, polyester and polyurethane. Tehy are also used as a plasticizer in vinyl automotive upholstery and in cellulose acetate articles. Other phosphate esters derived from DPP are methyl diphenyl phosphate; triphenyl phosphate; trixylenyl phosphate; isodecyl diphenyl phosphate; cresyl diphenyl phosphate; isopropylphenyl diphenyl phosphate.
APPEARANCE
Clear to yellow liquid
90.0% min
COLOR, APHA
60 max
0.2% max
Flame Retardant are substances that can be chemically inserted into the polymer molecule or be physically blended in polymers after polymerization to suppress, reduce, delay or modify the propagation of a flame through a plastic materials. There are several classes of flame retardants; Halogenated Hydrocarbons (Chlorine and Bromine containing compounds and reactive flame retardants), Inorganic flame retardants ( Boron compounds, Antimony oxides, Aluminium Hydroxide, molybdenum compounds, zinc and magnesium oxides ), Phosphorous containing compounds (Organic phosphate esters, phosphates, halogenated phosphorus compounds and inorganic phosphorus containing salts).